This interactive portal improves the analytic experience so you can easily interact with data.
Infographic: Social Determinants of Mental Health
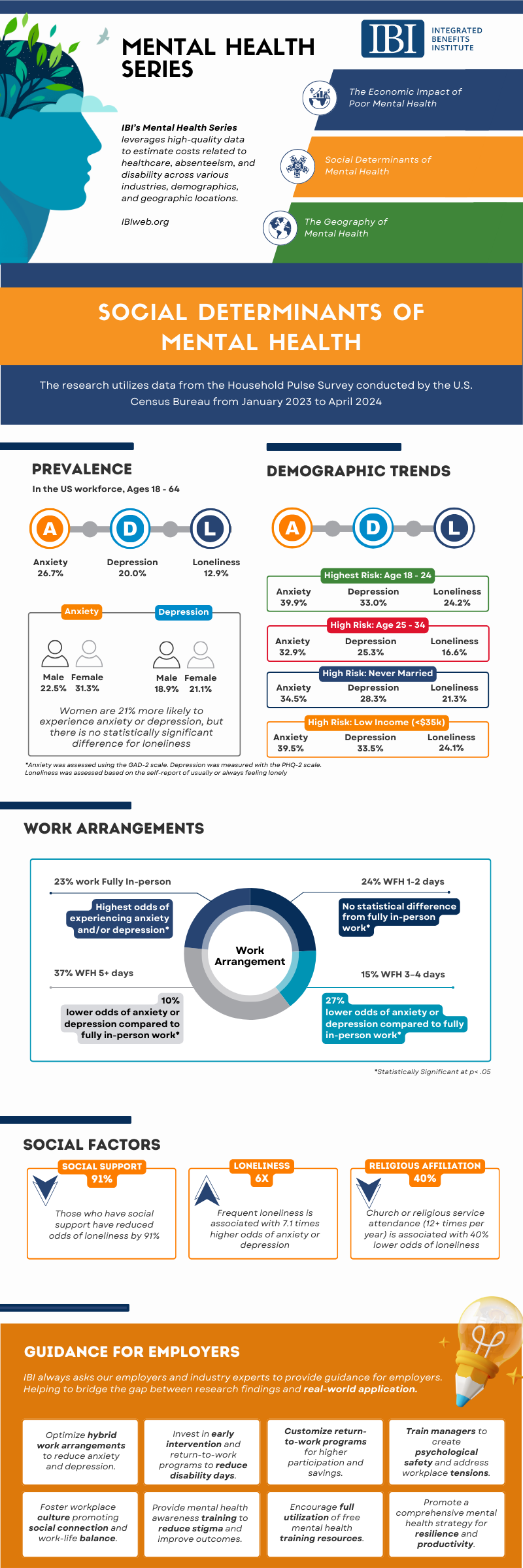
IBI’s latest study examines the prevalence and factors associated with anxiety, depression, and loneliness in the U.S. workforce. In the workplace, loneliness can manifest as social isolation from colleagues, leading to reduced job performance, lower job satisfaction, and increased turnover intentions. The work environment plays a critical role in either mitigating or exacerbating feelings of loneliness. Factors such as job design, organizational culture, and work arrangements (e.g., remote vs. in-office) can influence the extent to which employees feel connected to their colleagues.
Highlights from IBI's analysis:
- Clinically relevant anxiety was reported in 26.7% of the workforce, while clinically relevant depression was reported in 20.0%.
- 12.9% of the workforce indicated experiencing frequent loneliness assessed with an indication of usually or always experiencing loneliness.
- Those who worked fully in-person were the most likely to experience anxiety or depression.